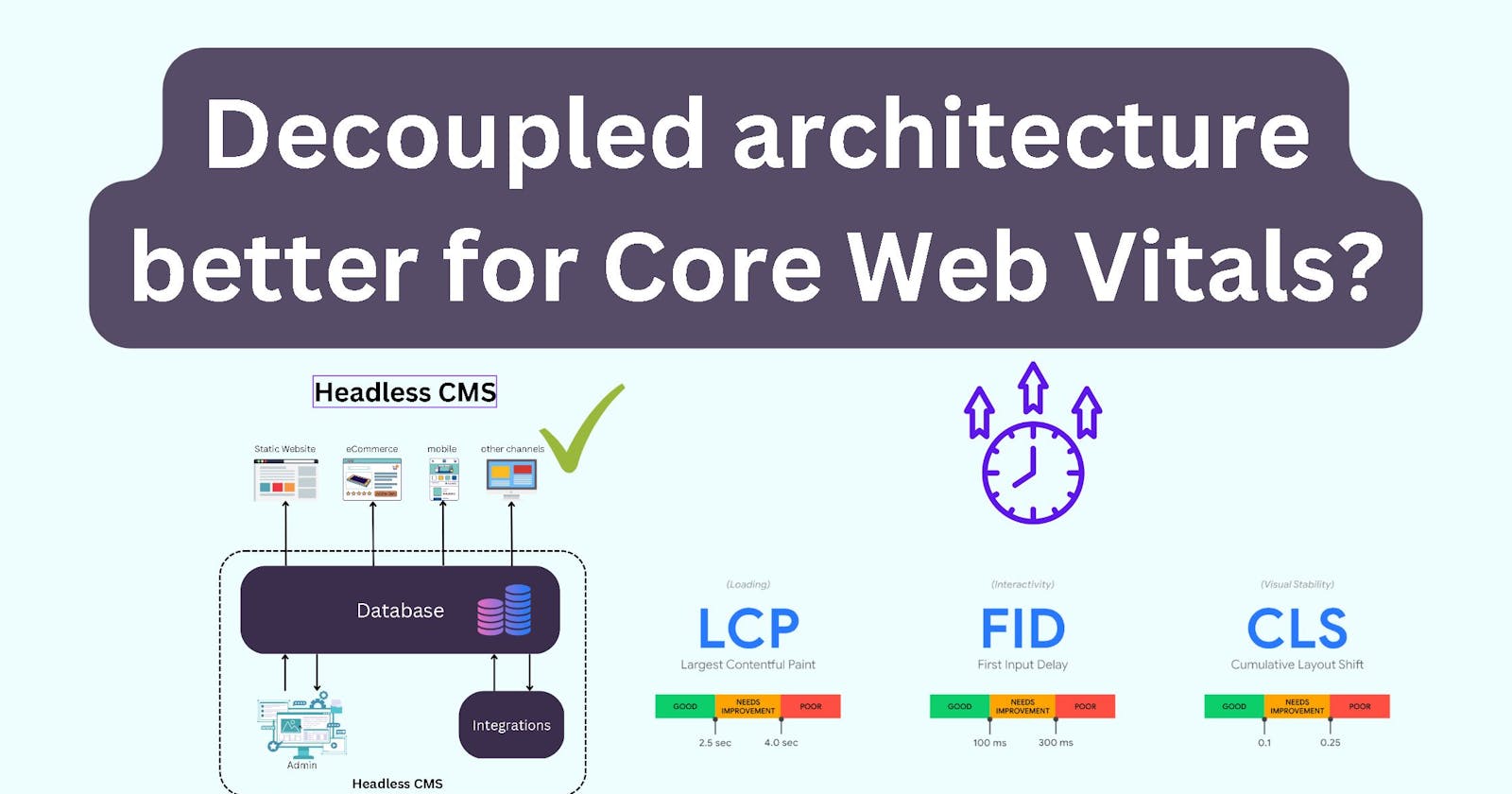
The Case for Headless CMS: How a Decoupled Architecture Can Boost Your Core Web Vitals Scores
The Context
First, let's define what Core Web Vitals (CWV) are.
Simply put, they are a set of metrics that measure the performance, security, and accessibility of a website.
Google introduced Core Web Vitals in May 2021 as a way to help website owners improve the user experience of their websites and provide a better overall experience for users.
But why does Google care about Core Web Vitals?
The answer is simple: they are a key factor in determining the quality of a website and its ranking in search results.
Websites that provide a good user experience are more likely to rank higher in search results, as they are more likely to be used and shared by users.
This is why improving your Core Web Vitals scores can have a direct impact on your search ranking.
How do traditional CMS (non-headless) fare in the context of Core Web Vitals?
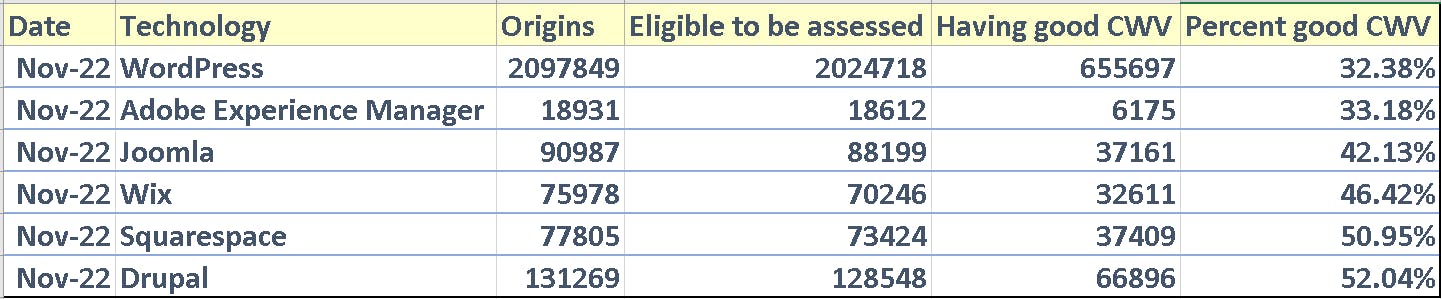
Take a look at CWV report of some of the popular Content Management Systems.

source: cwvtech.report
The November 2022 httparchive report on Core Web Vitals scores for various content management systems (CMSs), including WordPress, Adobe Experience Manager, Joomla, Wix, Squarespace, and Drupal, provides an overview of the average Core Web Vitals scores of websites using these technologies
Squarespace had the highest percentage of websites with good Core Web Vitals scores, at 50.95%. Drupal had the second-highest percentage, at 52.04%. WordPress had the lowest percentage of websites with good Core Web Vitals scores, at 32.38%.
In fact, the scores haven't changed much since May '21.
To determine why it is difficult to improve the Core Web Vitals of websites powered by non-headless CMS it is important we understand Core Web Vitals.
Core Web Vitals - an overview

source: web.dev
There are three main Core Web Vitals that are currently being measured:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This measures the loading performance of a page and indicates how quickly the main content of the page is visible to the user.
First Input Delay (FID): This measures the interactivity of a page and indicates how long it takes for the page to become interactive after a user first interacts with it.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): This measures the stability of a page and indicates how much the layout of the page shifts as it is loading.
Google has set specific thresholds for each of these Core Web Vitals, and websites that meet or exceed these thresholds are considered to be providing a good user experience.
Measurement | What to aim for |
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) | A load time of 2.5 seconds or less |
First Input Delay (FID) | An input delay of less than 100 milliseconds |
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) | A score of less than 0.1 |
By focusing on improving your Core Web Vitals scores, you can improve the overall quality of your website and deliver a better user experience for your visitors.
How to measure Core Web Vitals?
The easiest way is to use the pagespeed tool.
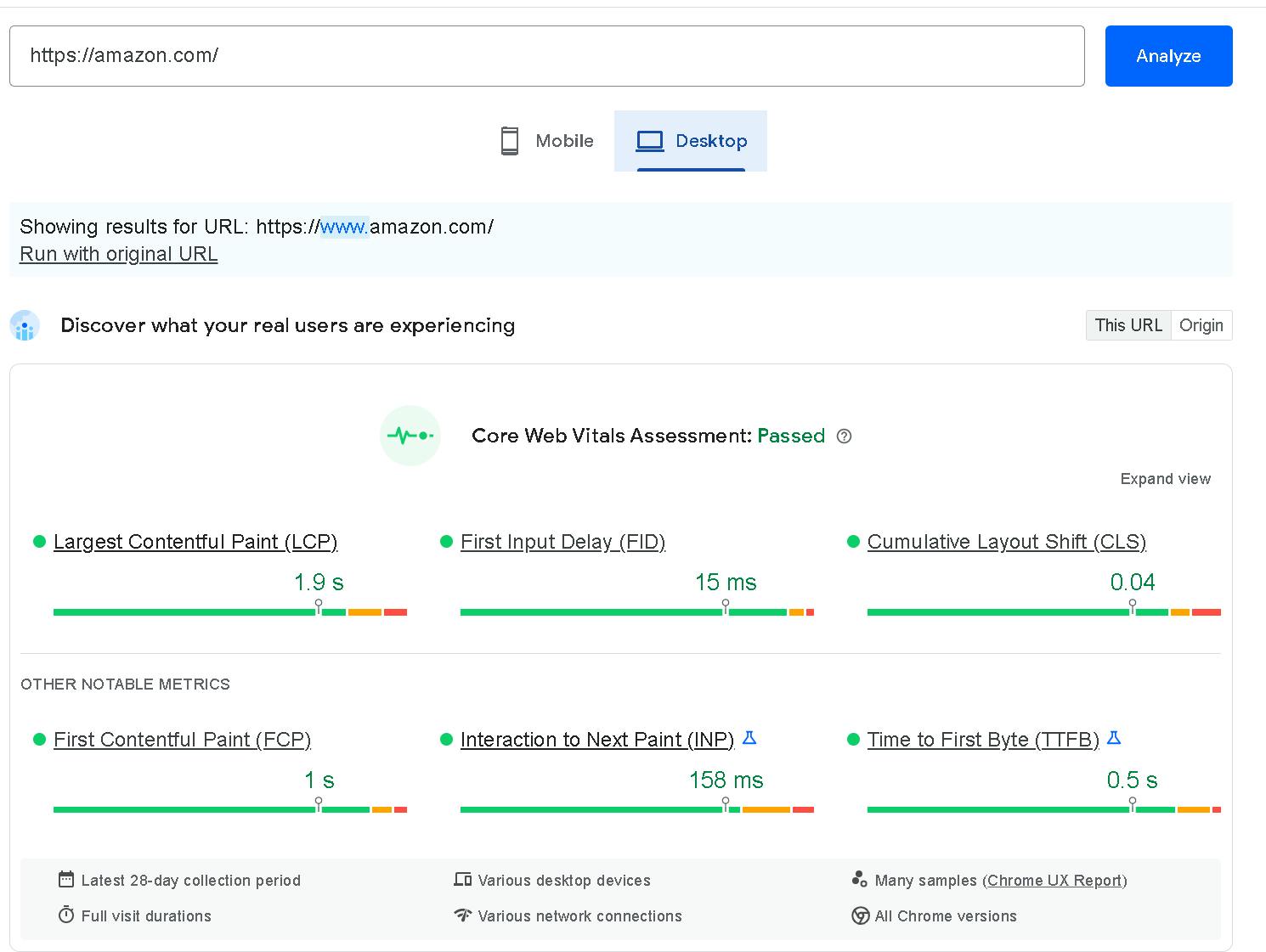
Check out the Core Web Vitals Assessment of amazon.com
How measuring and improving Core Web Vitals can help a website/business?
CWV Case Study - Rakuten 24
There are several case studies published on this. But one case study is relevant to our topic of discussion.
Rakuten 24's investment in Core Web Vitals increased revenue per visitor by 53.37% and conversion rate by 33.13%
After analyzing homepage data, Rakuten 24 found that a good LCP score can lead to:
An increase of up to 61.13% in conversion rate.
26.09% in revenue per visitor.
11.26% in average order value.
A good FID score can lead to an increase of up to 55.88% in conversion rate.
How did Rakuten do this?
Optimized JavaScript and resources
Optimized images
Optimized CLS
At the risk of generalizing all traditional CMS, Optimizing JavaScript and CSS may be more challenging in traditional content management systems (CMSs) compared to other approaches.
And this is why I believe Headless CMS may be better suited for optimizing Core Web Vitals, as they offer more flexibility and control over the user experience and performance of the website
Here's why...
The case for Headless Content Management Systems
A headless CMS is a content management system that separates the front-end interface (the "head") from the back-end content management system (the "body").
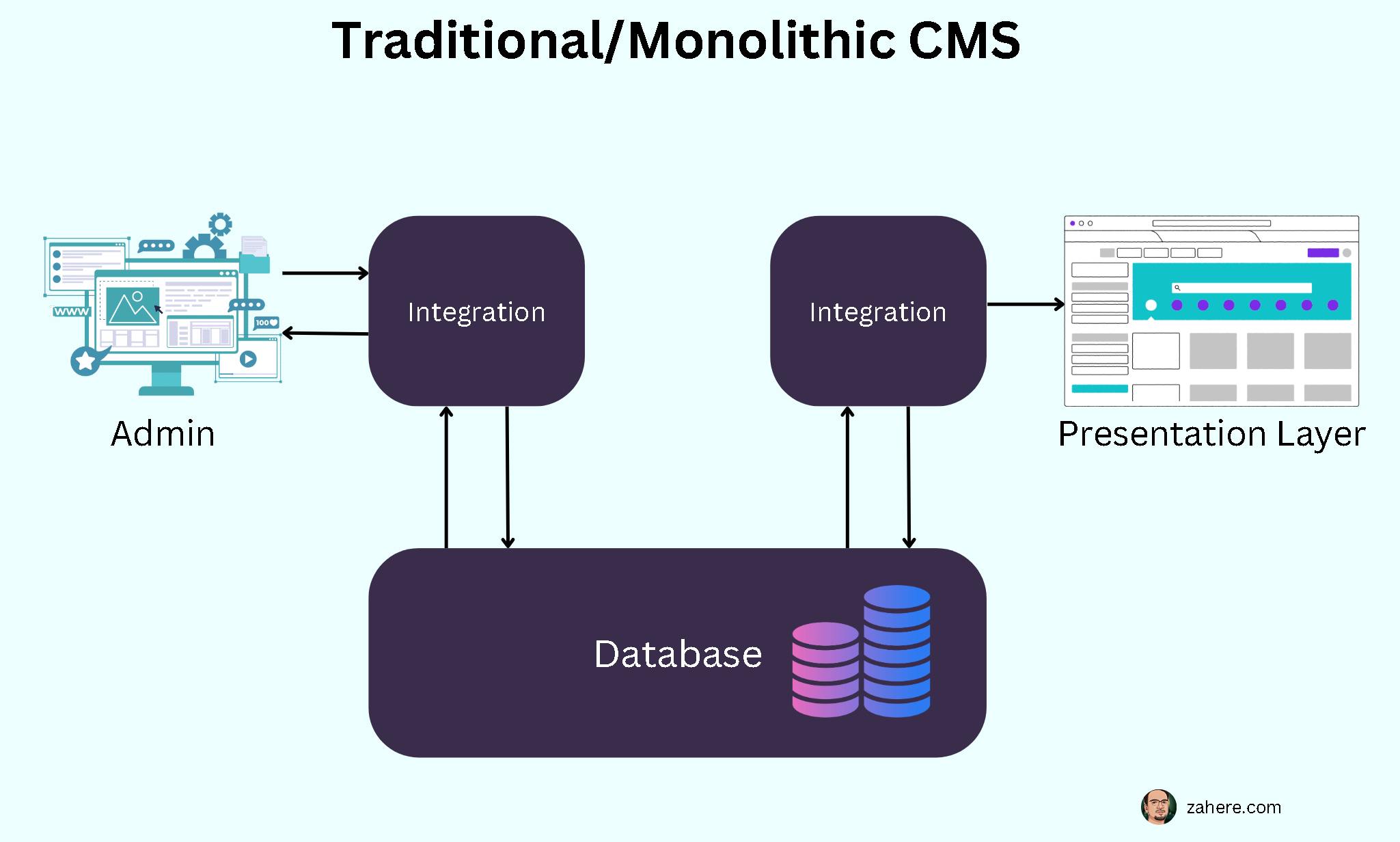
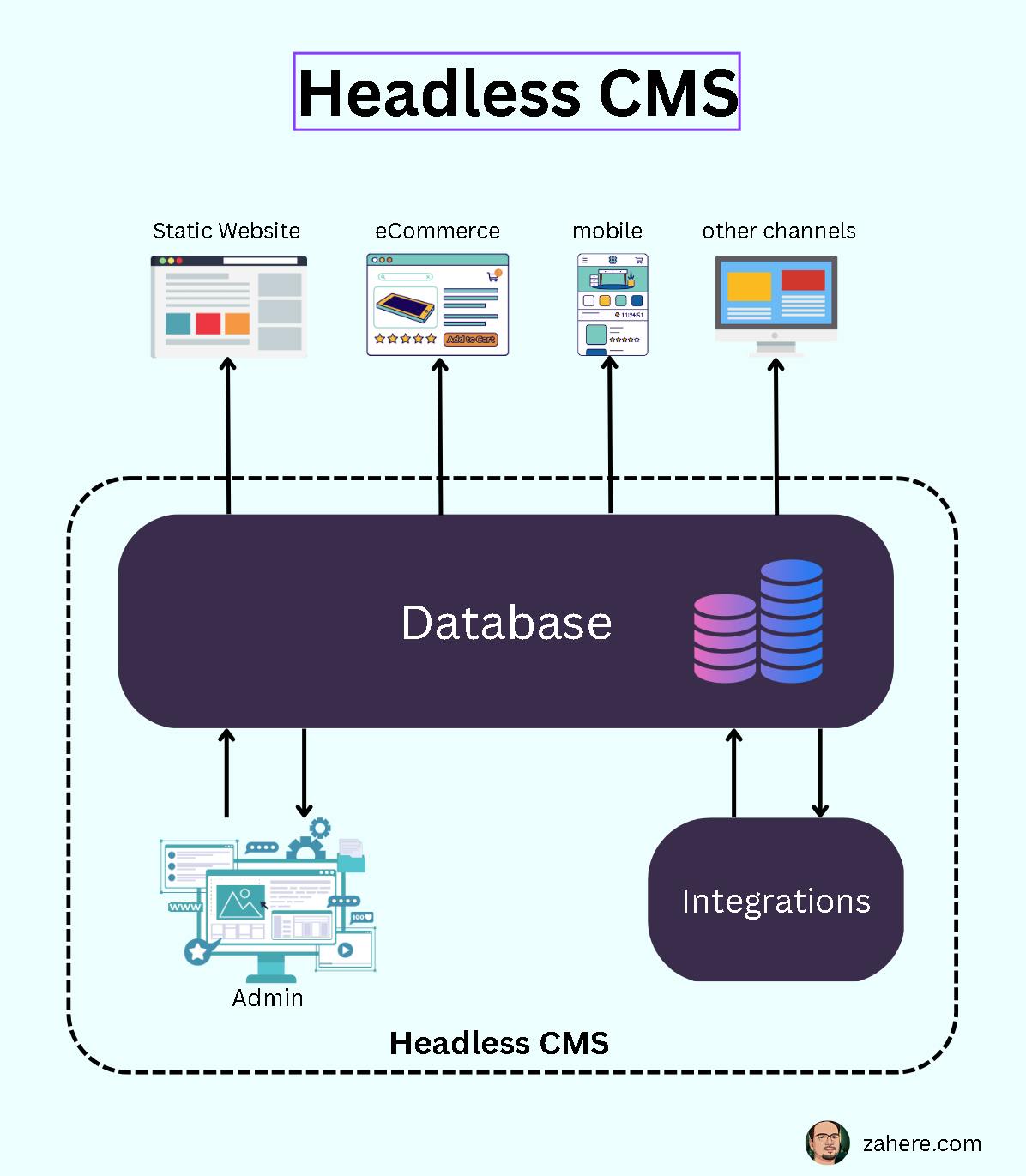
Here are a few specific ways in which a headless CMS can help you improve your Core Web Vitals scores:
Flexibility: With a headless CMS, you can choose the best technology stack for your needs and deliver content to any device or platform. This can help you deliver a better user experience and improve your Core Web Vitals scores.
Better control over the user experience: A headless CMS gives you more control over the user experience, as you can build custom interfaces and experiences without being tied to a particular platform or framework. This can help you optimize your website for Core Web Vitals and deliver a better user experience.
Enhanced scalability: A headless CMS allows you to easily scale your website to meet the needs of your audience, without being limited by the capabilities of a particular platform. This can help you deliver content quickly and efficiently, which is important for Core Web Vitals.
In conclusion, a headless CMS can be a powerful tool for improving your Core Web Vitals scores and delivering a better user experience for your website visitors. By leveraging the benefits of a headless CMS, you can take control of the performance of your website and improve its ranking in search results.
If you liked my content, do kindly like and share in your network. And don't forget to subscribe to the newsletter to NEVER miss an article.